MY ARTICLE RELATED UTERINE FIBROIDS, CAUSES, REASONS, SYMPTOMS, SIZES, COMPLICATIONS, TREATMENT
Cervical fibroids are a common type of cancer-free tumor that grows in or on your uterus . Not all fibroids cause symptoms, but when they do occur, the symptoms include heavy bleeding, back pain, frequent urination and pain during sex. Smaller fibroids do not require frequent treatment, but larger fibroids can be treated with medication or surgery.
- DEFINITION
- CAUSES
- SYMPTOMS
- UTERINE FIBROIDS AND PREGNANCY
- DANGEROUS SIZE
- COMPLICATIONS
- DIFFERENT TYPES
- DIAGNOSIS
- TREATMENT
FIBROIDS DEF:
Fibroids are a woman's or developing abnormal growth. Sometimes these tumors become very large and cause severe abdominal pain and heavy periods. In other cases, they do not cause any signs or symptoms. The growth is usually benign, or non-cancerous. The cause of fibroids is unknown.
Fibroids are also known by the following names:
Leiomyomas
myomas
Cervical myomas
Fibromyalgia
Fibroids range from seedlings, invisible to the human eye, to a massive mass that distorts and expands . You may have one fibroid or multiple. In severe cases, multiple fibroids can enlarge. It reaches the rib cage and causes weight gain.
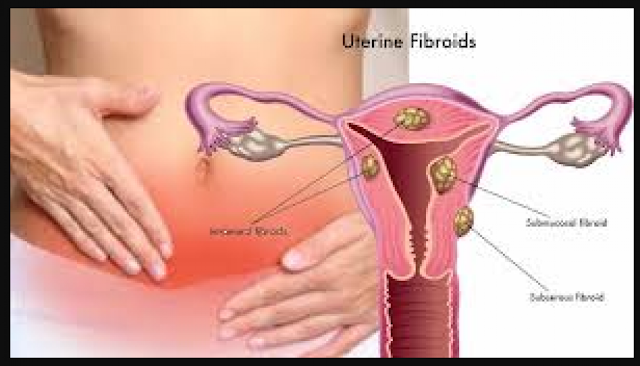
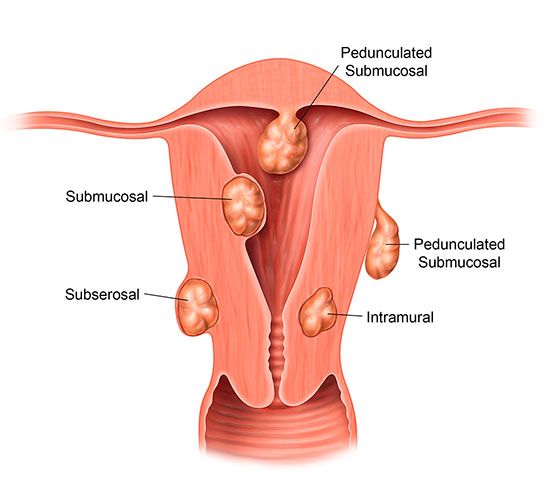
What Are The Different Types Of Fibroids?
The type of fibroids a woman develops depends on its location or in uterus.
1- Intramural fibroids:
Intramural fibroids are the most common type of fibroids. These are found inside the type muscle wall. Intramural fibroids increase and dilate your womb.
2- Subserosal fibroids:
Subserosal fibroids form outside your uterus, called the serosa. They are big enough to put your womb aside.
3- Pedunculated fibroids:
Subcerosal tumors develop on a stem, a thin base that supports the tumor. When they do, they are called pedunculated fibroids.
4- Submucosal fibroids:
These types of tumors develop in the middle muscle layer or myometrium of your uterus. Submucosal tumors are not as common as other types.
CAUSES OF FIBROIDS:
The cause of cervical fibroids is not known to physicians, but research and clinical experience suggest these factors:
Genetic modification:
Most fibroids contain genes that are different from normal cervical muscle cells.
Hormones:
Estrogen and progesterone, two hormones that stimulate the growth of the lining of the uterus during each structure cycle in pregnancy preparation, promote the growth of fibroids.
Menopause:
Fibroids contain more estrogen and progesterone receptors than normal uterine muscle cells. After menopause, fibroids decrease as the production of hormones decreases.
Other growth factors:
Ingredients that help the body maintain tissues and growth factors such as insulin affect the growth of fibroids.
Extracellular matrix (ECM):
ECM is a material that holds mortar-like particles between bricks. In fibroids, the ECM expands and makes them fibrous. ECM also stores growth factors and causes biological changes in cells.
Physicians believe that uterine fibroids develop from the stem cell in the smooth muscle tissue of the (myometrium). A single cell divides repeatedly, eventually forming a solid, rubbery mass separated from the surrounding tissue.
The growth patterns of cervical fibroids vary - they grow slowly or rapidly or they can be the same size. Some fibroids may grow, while others may shrink on their own.
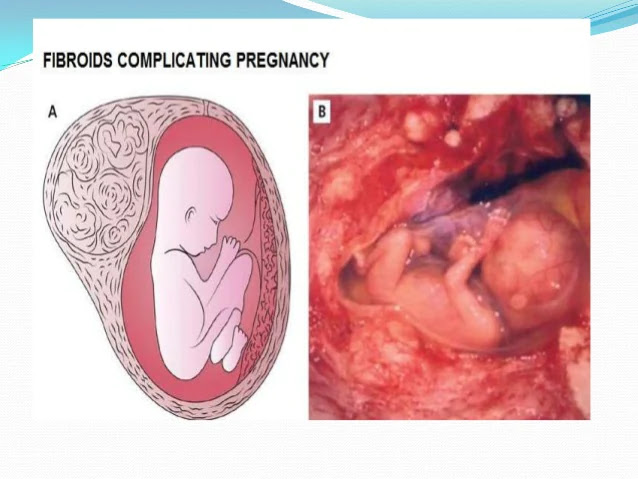
UTERINE FIBRODS AND PREGNANCY:
While fibroids do not interfere with ovulation, some studies suggest that they may reduce fertility and lead to pregnancy outcomes. In particular, submucosal fibroids, which deform the inner lining of the uterus, are strongly associated with decreased fertility. Sometimes, fibroids cause recurrent miscarriages. If they are not removed in these cases, the woman may not be able to manage the pregnancy.
Most fibroids present during pregnancy shrink or disappear after pregnancy because uterus goes to normal size.
Fibroids also increase the risk of certain pregnancy problems such as placental abruption,
- fetal growth restriction and premature labor.
- Miscarriage
- Effect on birth status
- Damage to the placenta
- Premature birth
- Bleeding
SYMPTOMS:
Most women with fibroid have no symptoms. In those who do, the symptoms are influenced by location, size, and number of fibroids.
In women with symptoms, the most common signs and symptoms of cervical fibroids are:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Menstruation lasts more than a week
- Pelvic pressure or pain
- Difficulty in emptying the bladder
- Constipation
- Back pain or leg pain
- Rarely, a fibroid can cause severe pain and begin to die when its blood supply is exceeded.
- Frequent urination (this happens when fibroids put pressure on your bladder).
Fibroids Cancer?
It is very rare for fibroid to develop into cancer or a malignant tumor. In fact, one in 350 women with fibroid will develop malignancy. There is no 100% able reversible test to detect cancers associated with rare fibroids. However, individuals with a rapid increase in cervical fibroids or fibroids that develop during menopause should be assessed immediately.
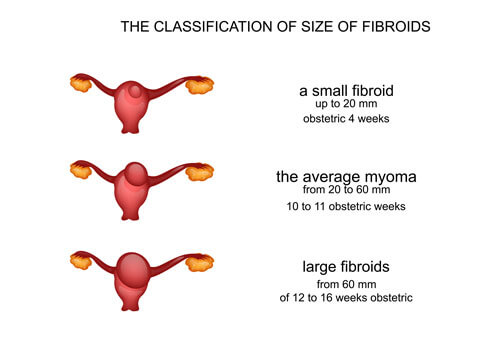
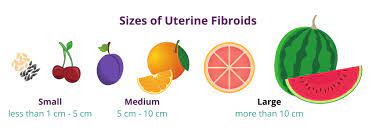
Which size of fibroids dangerous?( How big can fibroids get?)
Cervical fibroids range in size from watermelon to coin. According to doctor's opinion, Fibroids grow in single nodules or clusters and range in diameter from 1 mm to 20 cm. Even a very large fibroid can cause it to expand to a size equal to that of the third trimester of pregnancy. Fibroids can further develop into a group of very small fibroids or form a larger, dominant fibroid.
Fibroid size comparison:
Use the following guide as a reference point to normalize the size of small, medium and large fibroids.
Small (> 1 cm - 5 cm)
The size of a pea is lime.
Medium (5 cm - 10 cm)
Peach size for a large lemon.
Large (10 cm +)
From mango size to watermelon.
How are cervical fibroids diagnosed?
In many cases, fibroids are first detected during a routine examination with your women's healthcare provider. They can be seen during a pelvic exam and during a gynecological exam or during prenatal care. Your description of frequent heavy bleeding and other associated symptoms may alert your healthcare provider to consider fibroids as part of the diagnosis. Several tests can be done to diagnose fibroids and determine their size and location. These tests may include:
Ultrasonography:
This non-invasive imaging test creates an image of your internal organs with sound waves. Depending on the size, ultrasound can be done by transvaginal or transvaginal route.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
This test uses magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of your internal organs.
Computed tomography (CT):
CT scan uses X-ray images to create a detailed picture of your internal organs from multiple angles.
Hysteroscopy:
During hysteroscopy, your provider uses a device called a scope (thin, flexible tube with a camera at the end) to see the fibroids inside your uterus. The scope goes through your vagina and cervix into your uterus.
Hysterosalpingography (HSG):
This is a detailed x-ray where the contrast material is injected first and then a x-ray. It is most often used in women undergoing infertility evaluation.
Sonohysterography:
In this imaging test, a small catheter is placed trans vaginally and saline is injected through the catheter into the cervical cavity. This extra fluid helps to create a clearer picture of your uterus just like what you see during a standard ultrasound.
Laparoscopy:
During this test, your provider will make a small incision (incision) in your abdomen. A thin and flexible tube is inserted with the camera at the end to closely examine your internal organs.
Fibroids Treatment:
If you have cervical fibroids, you may not need treatment. It all depends on whether they give you any problems.
Not all fibroids grow. The elderly may also have no symptoms and most will shrink after menopause.
However, you and your doctor should check their growth, especially if you develop symptoms such as bleeding or pain. That is why you should have a pelvic exam at least every year.
1- Hormone Therapy:
To help prevent the growth of fibroids, your doctor may recommend that you stop taking birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy. In some cases, although hormones can cause fibroids to grow, your doctor may prescribe birth control pills to help control bleeding and anemia from fibroids.
2- GnRH Antagonists :
GnRH is a hormone that your body naturally makes. GnRH antagonists keep your body in menopause until you take them by reducing the estrogen that promotes the growth of cervical fibroids. These drugs are expensive.
You should not take them for more than 6 months as they can make you osteoporosis, which can make your bones very weak. Your doctor may also prescribe a lower dose of progestin or a lower dose estrogen / progestin pill to reduce osteoporosis.
3- SERMs:
SERMs are a type of drug that works on your estrogen levels. (SERM stands for Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator.) They can shrink fibroids without causing menopausal symptoms. But researchers still do not know how well they work for this purpose.
4-Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GNRH) agonists:
These drugs can be taken by nasal spray or injection to work by compressing your fibroids. These are sometimes used to shrink fibroids before surgery, which makes it easier to remove the fibroids. However, these drugs are temporary and if you stop taking them, the fibroids will grow back.
There are many possibilities that you and your doctor can consider.
1- Fibroid embolization can shrink a fibroid:
Your doctor will inject polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) into the arteries that feed the fibroids. PVA blocks the blood supply to the fibroid, thereby reducing it. It is not surgery, but you may have nausea, vomiting and pain for the first few days so you will have to spend many nights in the hospital.
2- Endometrial Ablation:
This is the way doctors destroy the membrane of uterus to reduce the bleeding associated with small fibroids.
3- Myomectomy:
Is surgery to remove fibroids. If you are thinking of becoming pregnant, your doctor may recommend other procedures. But it can also cause scarring that can lead to infertility. You should wait 4 to 6 months after surgery before attempting to conceive. In most women, the symptoms go away after a myomectomy. But in others, fibroids come back. Whether this works depends on how many fibroids you have and whether the surgeon can remove them all.
Myomectomy may be abdominal surgery, or your surgeon may use a hysteroscope or laparoscope to remove fibroids without making a large incision in your abdomen. There is also a new method that uses MRI-guided intensive ultrasound power to detect fibroids and shrink or destroy them.
4- Hysterectomy:
Cervical surgery is surgery to remove it. Most women do not need such intensive treatment. You cannot get pregnant after this operation.
5- Radio Frequency Ablation (RFA):
It is a safe and effective treatment for women with symptomatic uterine fibroids and can be given through laparoscopic, transvaginal or trans cervical procedures.
6- Fibroid surgery:
There are many factors to consider when talking about different types of surgeries to remove fibroids. Not only does the size, location and number of fibroids affect the type of surgery, but your desires for future pregnancy can also be an important factor when developing a treatment plan. Some surgical options protect uterus and allow you to become pregnant in the future, while other options may damage or remove uterus.
Medications can cause side effects:
- Some may not be right for you. Before starting a new medicine pill, talk to your healthcare provider about all the pills you are taking for other health conditions and for your complete medical history. If you experience side effects after starting a new medicine, call your provider to discuss your options.
- Surgical treatment of fibroids is always risky. Any surgery can cause you infection, bleeding and any risks associated with surgery and anesthesia. An additional risk of fibroid removal surgery is having a future pregnancy.
- Some surgical options can prevent future pregnancies.
- Myomectomy is a procedure that only removes fibroids that allow for future pregnancies. However, women who have had a myomectomy may need to deliver their babies by cesarean (C-section) in the future.
1- Homeopathy is very effective in treating cervical fibroids. Of all the possible options, homeopathy is a non-surgical treatment for fibroids. Homeopathic medicines are slow but sure treat of increase in fibroids. Over time, the fibroids disappear completely. It is a very effective and convenient treatment for fibroids.
2- There are over a dozen homeopathic remedies for treating fibroids. All are equally effective when prescribed. Indications for homeopathic medicines depend on the compatibility of medicines with the patient's symptoms. Once a good match is found, the prescribed remedy must cure the patient. I can say with full confidence that some drugs are very commonly prescribed.
1. Phosphorus-
The best homeopathic medicine remedy for fibroids with excessive and chronic bleeding.
Phosphorus is one of the best homeopathic remedies for cervical fibroids when the cervical fibroids have prolonged and abundant bleeding. There may also be bleeding in the middle. The patient has an anxious mood and cries even before menses.
2. Sabina-
The best homeopathic medicine remedy for cervical fibroids with clotted bleeding.
Sabina is one of the best homeopathic remedies for fibroids when black or black clots are released along with the blood. Blood color rich and bright. Bleeding is worse than speed. There will be pain when going from the sacral area. Cervical pain often radiates down and to the thighs.
3. Calcarea Carb-
The best homeopathic remedy for fibroids with cold ,chilly patients.
When cervical fibroids are accompanied by cold and cold sweats, Calcarea is one of the best homeopathic medicine remedies for carb fibroids. A patient with calcareous carb is usually , flawless, affordable and sweats well. There may be a sour smell about the patient. Menses too high and too long. Before menses, is burning and itching in vulva. There may be bite pain in the cervical region at the time.
4. sepia-
The best homeopathic medicine remedy for cervical fibroids to reduce irritation, lethargy and pain.
Sepia is one of the best homeopathic remedies for cervical fibroids when there are psychological symptoms of irritability and indifference towards family members. There is severe pain in the lower abdomen. patient Feels like it saves everything. He feels he has to cross his legs to stop the protrusion of the material. Periods are too late and too short. There may be pain during intercourse.
5. Thyroidism -
One of the best homeopathic medicine remedy for cervical fibroids that are outstanding for obsess patients of fibroids.
The thyroid gland is often under active, useless.. Tumors may also be in patient's breast.
Thanks for review my uterus fibroids article.
For health related information visit my channel:










2 Comments
Today femlz major problm..knowldgeable infrmation Dr shiba detail zbrdst 👍👍👍👍👍
ReplyDeleteZbrdst
ReplyDelete