- Allergies.
- Asthma.
- Depression.
- Lack of sleep.
- Worry.
- Note that diabetes is not included in this list.
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS?
Eczema of all kinds causes itching and redness, but AD is the most severe and chronic. Other types of eczema:
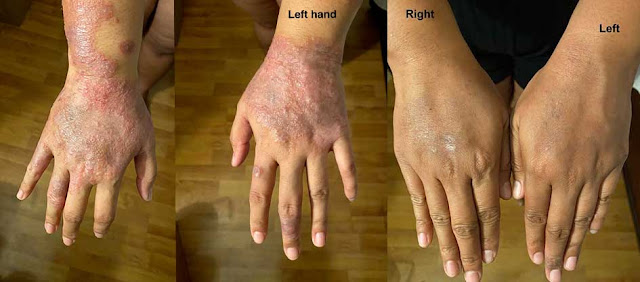
1- Hand Eczema:
Hand eczema only affects your hands and is often caused by frequent exposure to irritating chemicals.
2- Contact Dermatitis:
Contact dermatitis is a skin irritation caused by certain irritants.
Small blisters on the skin.
3- Dyshidrotic Eczema:
Is a type of eczema that develops only on your toes, palms and soles of your feet.
4- Neurodermatitis (lichenification).
Neurodermatitis is characterized by thick patches of skin caused by repeated rubbing or scratching.
5- Namular Eczema:
Namular eczema is a chronic condition that often causes itchy coin-sized spots.
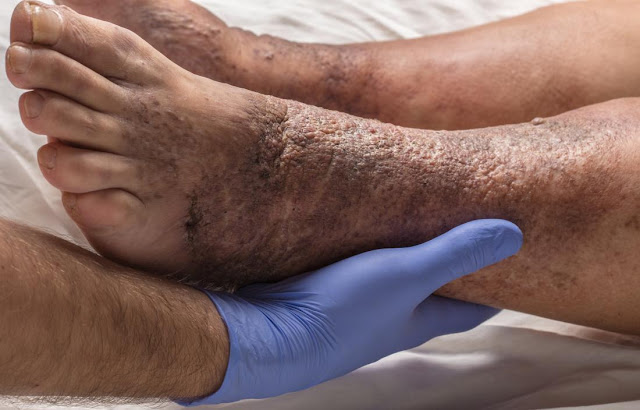
6- Stasis Dermatitis:
Stasis dermatitis is a type of skin irritation that develops in people with poor blood circulation, usually in the lower legs.
Atopic Dermatitis Vs Eczema:
AD is often referred to as eczema, a term used to describe a wide range of skin conditions. "Dermatitis" refers to skin conditions and "atopic" refers to diseases caused by allergic reactions.
As an atopic disease, AD falls under the same classification:
- Food allergies
- Hay fever
- Asthma
SYMPTOMS IN INFANTS, CHILDREN, ADULTS
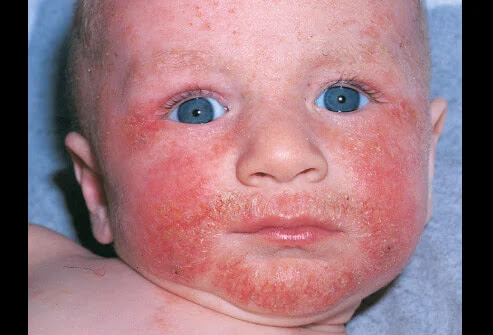
1- Symptoms In Infants:
Infants may have symptoms:
- Dry, itchy, scaly skin
- Rash on the scalp or cheeks
- Bubble and clear fluid-secreting rash
- Children with these symptoms may have difficulty sleeping due to itchy skin.
- Scratching in children with AD can also lead to skin infections.
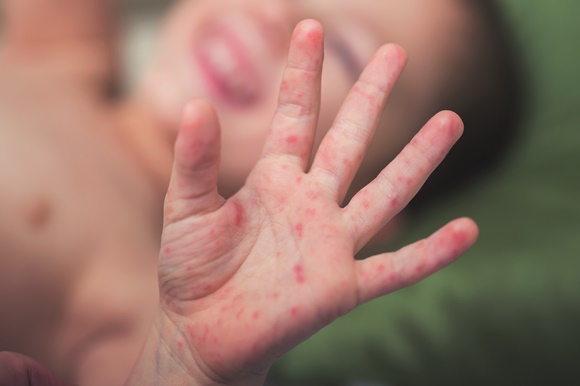
2- Symptoms In Children:
Symptoms in children may include:
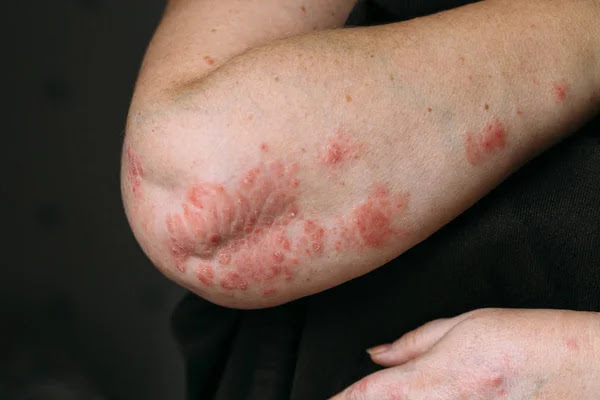
- Rash on the elbows, knees or both folds
- Scaly spots of skin instead of rash
- Pale or dark skin patches
- Thick, leathery skin
- Very dry and scaly skin
- Rash on the neck and face, especially around the eyes
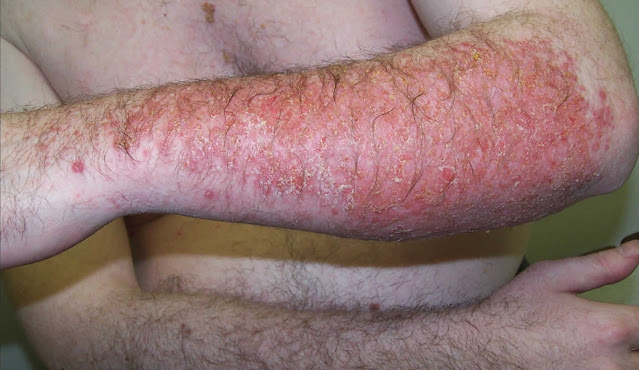
3- Symptoms In Adults:
Adult skin with AD is very dry and scaly. In a 2021 survey published by the Eczema Society of Canada, 71 percent of people with moderate or severe AD rated their itching as 7 out of 10 or more.
According to the American Academy of Dermatology Association, adults get AD in different places than children. Commonly affected areas:
- Behind the knees
- Elbow curves
- Behind the neck
- Face
Adults also have more symptoms around their eyes.
Adults with AD in childhood may have easily irritated discolored skin or skin patches. Some people with AD in childhood may not show symptoms for many years until they return to puberty.
CAN ATOPIC DERMATITIS GO AWAY?
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is a condition that causes your skin to become red and itchy. It is common in children but can occur at any age. Atopic dermatitis is chronic (chronic) and periodically inflammatory. It can occur with asthma or hay fever. No treatment has been found for atopic dermatitis.
DIAGNOSIS:
Diagnosis Of Eczema And Dermatitis
Different types of eczema and dermatitis are very similar on the skin. The rash is often red, scaly and dry but can turn into cracks, rash and blisters. Most rashes are very itchy and people find it difficult to scratch.
Our doctors have been pioneers in the diagnosis of contact dermatitis since patch testing was brought to the United States in the 1930s and the technology has improved. This allergy test is specifically designed to determine the cause of contact dermatitis without the use of needles. Patch testing is the only reliable way to determine which substances cause an allergic reaction when in contact with the skin.
1- Physical Examination And Medical History:
A dermatologist will carefully examine your skin during a physical exam. The pattern, location and form of the rash provide important information to our doctors about its causes.
Your doctor may ask questions about when symptoms appear, what parts of the body they affect, and whether the rash is persistent or recurrent. They also want to know if there are any noticeable patterns of seasonal variation or the appearance of rashes when certain perfumes are used or after exposure to certain metals or fabrics. . Knowing that someone else in your family has been diagnosed with eczema or dermatitis can help doctors better understand your diagnosis.
The doctor may also ask about personal hygiene products that you use in your home. Many cosmetics, moisturizers and soaps contain irritants that can cause eczema and dermatitis. Our dermatologists may recommend non-irritating, odorless products that contain low levels of preservatives. Often, these are available at drugstores in the same price range that you would normally buy.
2- Patch Test:
If dermatologists suspect that allergic dermatitis may be the cause of your rash, the patch test is the most effective diagnostic tool. Generally, the exam requires three visits to the doctor's office within a week.
In patch testing, several thin metal or flexible plastic chambers are mounted on strips or panels. Each room contains a small amount of allergen. Allergens used in the test are found in products that are used regularly in daily activities. Your doctor may prescribe a variety of chemicals depending on the distribution of the rash and the specific substances you are exposed to at home or at work.
The test panels are placed on the skin of your back and covered with tape. Your doctor will record the location of each allergen on your skin. The taped panels are left on for about two days so that the body can detect and respond to a potential allergen. You can do most of your daily routine by wearing a tape panel, but you should avoid exercise, bathing and other activities that moisturize the patch.
After two days, the panels are removed and a note of any areas of irritation is made. A physician may not record the final result for up to four days to allow for delayed reactions. At the final reading, our doctors will perform a test to match the reaction signs on the skin with the substance placed there. Redness along with increased skin or rash at the site of the tested allergens may help your dermatologist identify the source of the allergic reaction and diagnose allergic dermatitis.
3- Skin Biopsy:
Sometimes, a dermatologist will need to remove a small piece of skin for a lab test. If doctors are unable to diagnose your condition during a physical exam or patch test, a procedure called a biopsy is usually needed.
Skin biopsy is a minor procedure performed in a doctor's office. Doctors usually inject a local anesthetic to numb the skin and use a scalpel, sharp blade or punch to remove a small portion of the rash. The biopsy area is covered with a bandage and heals within a week.
In the lab, a pathologist who specializes in skin cells, called a dermatopathologist, examines the sample under a microscope to see if there is eczema or dermatitis or any other skin condition. The rash is responsible. Biopsy results take three to seven days.
TREATMENT OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS:
Atopic dermatitis may be persistent. You may have to try different treatments over months or years to control it. And even if treatment is successful, signs and symptoms may return (inflammation).
It is important to identify the condition before you start treatment. If regular moisturizing and other self-care steps do not help, your doctor may recommend one or more of the following treatments:
DRUGS/ MEDICATIONS:
- Creams that control itching and heal the skin. Your doctor may prescribe a corticosteroid cream or ointment. After moisturizing, apply as indicated. Overuse of this drug can lead to side effects such as thinning of the skin.
- Other creams that contain drugs called calcinurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus (protopic) and pimecrolimus (Elidel), can affect your immune system. They are used by people over 2 years of age to help control skin reactions. After moisturizing, apply as indicated. Avoid strong sunlight when using these products.
These medications have a black box that warns of the risk of cancer. But the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology concluded that the risk-to-benefit ratios of topical pimecrolimus and tacrolimus are similar to other traditional therapies for persistent eczema and that data do not support kale use. - Drugs That Fight Infection:
Your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic cream if you have a bacterial infection, open sores, or cracks in your skin. He may recommend taking antibiotics for a short time to treat the infection.
For more severe cases, your doctor may prescribe corticosteroids - such as prednisone. These drugs are effective but are not used for a long time due to serious side effects.
- New Option For Severe Eczema:
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently approved a new, injectable biologic (monoclonal antibody) called Duplimab (Dupixent). It is used to treat people with serious illness who do not respond well to other treatment options. It's a new drug, so there is no long track record of how much it can help people. Studies have shown that it is safe to use if prescribed. It is very expensive treatment.
Effective, intensive treatment for acute atopic dermatitis involves wrapping the affected area with topical corticosteroids and wet bandages. Sometimes this is done in a hospital for people with extensive injuries because it is laborious and requires nursing skills. Or, ask your doctor about learning how to do this technique at home.
This treatment is used for people who do not improve with topical treatments or for rapid inflammation after treatment. The simplest form of light therapy (phototherapy) exposes the skin to a controlled amount of natural sunlight. Other forms include synthetic ultraviolet A (UVA) and narrow-band ultraviolet B (UVB) alone or in combination with drugs.
Although effective, long-term light therapy can have detrimental effects, including the risk of premature skin aging and skin cancer. For these reasons, phototherapy is less commonly used in young children and should not be given to infants. Talk to your doctor about the advantages and disadvantages of light therapy.
Talking to a therapist or other counselor can help people who are embarrassed or bored by their skin condition.
Relaxation, behavior change and biofeedback. These procedures can help people who are habitually scratching.
Lifestyle And Home Remedies:
To reduce itching and relieve inflamed skin, try these self-care remedies:
Your skin at least twice a day. Find a product or combination of products that work for you. You can try bath oils, creams, ointments or sprays. For children, the routine twice a day may be ointments before bedtime and creams before school. Ointments are more oily and have less stinging when applied. On the affected area. A non-prescription hydrocortisone cream, which contains at least 1 percent hydrocortisone, can provide temporary relief from itching. Do not exceed twice a day on the affected area after moisturizing. Medicinal creams Helps to improve skin using pre-moisturizer. Once your reaction has improved, you can use this type of cream less often to prevent inflammation.
- Take Allergy Or Anti-Itch Medicine:
Over-the-counter allergy medications (antihistamines) such as cetirizine (Zirtec) or fexofenadine (Allegra). Also, diphenhydramine (Benadryl, et al.) May help if the itching is severe. But it causes drowsiness, so it is better to sleep.
Try to press on the skin instead of scratching. Cover the itchy area if you can not stop from scratching. For children, it helps to trim their nails and wear gloves at night.
Covering the affected area with bandages can help protect the skin and prevent scratching.
sprinkle with baking soda, sweetened oatmeal or colloidal oatmeal — finely ground oatmeal (Avino, et al.) Made for baths. Let soak for 10 to 15 minutes, then let dry. Apply moisturizer while skin is still moist.
- Choose a mild soap without dye or perfume:
Use high fat and alkaline soap. Be sure to wash thoroughly with soap.
Hot, dry indoor air burns sensitive skin and exacerbates itching and scabs. A portable home humidifier or one attached to your furnace will add moisture to the air inside your home.
- Wear clothes with cool, soft textures:
Reduce irritation by avoiding clothing that is rough, tight or scratchy. Also, wear appropriate clothing in hot weather or during exercise to avoid excessive sweating.
- Treat Stress And Anxiety:
Stress and other emotional disorders can exacerbate atopic dermatitis. Accepting them and trying to improve your mental health can help.
HOMOEOPATHY TREATMENT OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS
1- SULPHUR:
I want to quote Misha Norland, because he writes so eloquently about sulfur! "Sulfur comes from within the earth . It's known as yellow crystals around volcanic holes or fumaroles, where hot gas cools and thrives and is in liquid form in active volcanoes . so K may be the man's head. And burning with philosophies.His problem is that he does not bring his principles or philosophy to earth "in the air",they have a strong tendency to hoarse.Even though they have just bathed, they still look dirty and develop red, dry, flaky skin, which is itchy There are two types of sulfur: one is outgoing, strong, solid and the other is calm, thin and not sure about it, but both types do not care much about their appearance. "
2- GRAPHITES:
Graphite is a carbon compound (such as diamond and charcoal) commonly used as 'lead' in pencils. It is a very useful remedy for crusty, moist, pale and sticky eczema; Occurs especially in the folds of joints such as the elbows, knees or groin. The skin can become very dry, cracked, red, itchy and painful.
Graphites 'type' is usually a shy person, his mood ranges from being light and cheerful to worrying about a lack of self-confidence. They are very sensitive and suffer from the kind of emotions that make it easy to shed tears through their favorite music or emotional movie and poor short-term memory. This remedy also strongly affects digestion and is suitable for overweight (or obese) patients.
3- CALC.CARB
The remedy is made from the calcium carbonate found in oyster shells. As a bivalve mollusk, oysters are one of the most ancient forms of life as well as one of the most popular dishes! Their compressed shells produce the limestone we use to build our homes and they also make beautiful pearls. It is a useful remedy for moisturizing, discharge eczema especially on the scalp and young children. Common Calc-Carb 'type' down-to-earth, hard working and alert.
They may also develop a more emotional type (as opposed to intellectual sulfur and lycopodium) and a strong anxiety or fear that others will see their confusion or lack of knowledge. When times are bad, it completely distances people from them! They are very prevalent and as children they feel insecure without the support of their parents. Even as adults, they like the company of people they know well and may shun strangers.
4- CICUTA VIROSA
Cicuta, or northern water hemlock, is a poisonous plant of the umbelliferae family (whose flowers are umbrella-shaped). Eczema forms a thick yellow film (like dried honey) and affects the cheeks, and head where there is inflammation and itching. It is also useful in treating seizures, hiccups, tremors, convulsions, convulsions or epileptic seizures.
These symptoms may appear after a head injury. The ‘type’ of cicuta is not well known, but they may seem too childish or immature at the same time distrustful of others, especially if they have been depressed in previous relationships. When ill, they generally prefer to stay away from companionship, perhaps even declaring that they have 'lost faith in humanity'.
5- SEPIA:
Sepia is a medicine made from the ink of cuttlefish; The cephalopod is a fascinating sea creature in the group. The animal uses camouflage and ink clouds to escape from predators.
Even patients who need sepia may want to avoid their condition, especially if it is high at work! It especially helps those suffering from chronic eczema of the nose, behind the ears and those with very dry skin.
Flames can occur during pregnancy or lactation, especially if there are other stressors such as increased emotional demands during that time.
The ‘type’ of sepia is most commonly seen in women, where they tend to get tired of overwork themselves, especially when trying to find a balance between career and motherhood. His power is flat; They are useless and unattached, even away from family members.
They feel better by being engaged or by intense exercise such as jogging or dancing. Physical activity is required to bring them out of a lethargic state. It has a broad preventive action and is also useful for morning sickness, hormonal complaints, painful and hot flushes during menopause.
6- NAT.MUR
Natrum moor is the Latin name for common salt, the chemical bond between sodium and chloride. It has a profound effect on the physiology of the human body, especially in the fluid systems;
Dehydration and weight loss are caused by increased salt loss through the kidneys and skin. Or on the other hand there may be watery tissue, edema and weight gain. It is used in homeopathy for eczema found on the beach, in the joints, and around the hair and mouth.
Natrum mur. type is naturally emotional, emotionally-oriented and sensitive- they are good listeners and prefer to listen to the problems of others rather than talking about their own problems. Their symptoms fall into unwanted love after grief, shock or rejection.
They have been worried about their misfortune for a long time after that. If this continues for a long time, they may go into a wall-off or emotional state, trying to protect themselves from re-injury.
7- LYCOPOIDUM:
Lycopodium is an ancient plant that originated in the Carboniferous era. At that time it was the size of a powerful tree, but withstood evolutionary change, it was reduced in size to a delicate plant. In homeopathy, it is used for eczema with bleeding, dampness or discharge. Complaints of the liver can affect the skin, armpits, limbs, back and neck and eczema.
ALWAYS USE ALL MEDICINES BY DOCTOR ADVISE
FOR MORE DETAIL ABOUT HOMOEOPATHY ,VISIT MY CHANNEL
DR.TAYYIBA AJ









0 Comments