WHAT IS OBESITY/ AND OVERWEIGHT? YPES OF OBESITY, CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, CHILHOOD OBESITY, DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT
Also known as obesity, carpal tunnel or obesity, it is caused by excessive accumulation of body fat, which usually results in the body consuming more calories than it consumes. High calories are stored in or adipose tissue. Being overweight, if moderate, does not mean being particularly obese, especially in muscular or large - individuals.
OBESITY MEANING / DEFINITION
OVERWEIGHT
TYPES
CAUSES
SYMPTOMS
CHILDHOOD OBESITY
DIAGNOSIS
TREATMENT
WHAT IS OBESITY / MEANING?
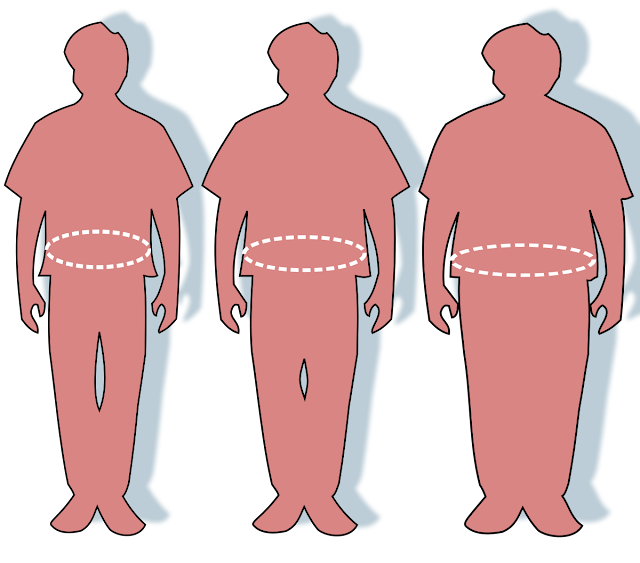
1- Obesity is an abnormal accumulation of 20% or more bodies in the average body weight of a person. Obesity is associated with an increased risk of disease, disability and death.
The branch of medicine that deals with the study and treatment of obesity is called bariatrics. As obesity has become a major health problem in the United States, bariatrics has become a specialized medical and surgical specialty.
2- Obesity has traditionally been defined as an increase in body weight in excess of 20 percent of a person's ideal body weight — as measured by a number of factors, including the lowest risk of death, such as: age, height, and gender. Depending on these factors, overweight can be defined as an increase of 15-20 percent over the ideal body weight. However, today the definitions of overweight and obesity are mainly based on measurements of height and weight — not illness. These measurements are used to calculate a number called the Body Mass Index (BMI). This number, which is central to determining whether a person is clinically defined as obese, is parallel to obesity but not a direct body measurement ***. The interpretation of BMI numbers is based on weight status groups such as underweight, healthy weight, overweight and obesity, which are adjusted for age. For all adults over 20, the BMI number is the same as for weight status; For example, a BMI between 25.0 and 29.9 is equivalent to being overweight and being obese at 30.0 and above. Unhealthy obesity (also known as acute, or severe, obesity) is defined as a BMI of 40.0 or higher.
OVERWEIGHT:
The term "overweight" is used in two ways. This is a way to tell if someone is overweight in a sense. The second meaning of "overweight" is more precise and refers to the state between normal weight and obesity.
TYPES OF OBESITY:
What are the four main types of obesity?
Brown University has identified four major types of obesity:
1- Group One: Diabetes.
Low levels of "good" cholesterol
High blood sugar level
98% of people in this group have diabetes
2- Group Two: Irregular diet.
People with overeating disorder have problems
60 percent said they could not control what they ate
92 percent reported eating when not hungry
3- Group Three: Mixed.
Low levels of junk food (only 7% say they ate when they were not hungry)
There is no other special factor
4- Group Four: Early Start.
Obesity from an early age
The 18-year-old had the highest BMI (average 32)
Highest pre-surgery BMI 58 (25 healthy, 30 obese)
CAUSES:
The balance between calorie intake and energy expenditure determines a person's weight. When a person eats more calories than they burn (metabolism), that person gains weight (the body stores extra energy like ***). If a person eats fewer calories than they metabolize, they will lose weight. Therefore, the most common causes of obesity are overeating and physical inactivity. Ultimately, body weight is a result of genetics, metabolism, environment, behavior and culture.
1- Physical inactivity.
Stable people burn fewer calories than active people. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) showed a strong link between physical inactivity and weight gain in both sexes.
2- Eat more.
Overeating can lead to weight gain, especially if the diet is high in or foods ,high in sugar (e.g., fast food, fried foods and sweets) have a high energy concentration (very low calorie foods). Epidemiological studies . Excessive foods have been shown to contribute to weight gain.
3- Genetics.
A person is more likely to be obese if one or both of their parents are obese. Genetics *** also affects hormones involved in regulation. For example, the genetic cause of obesity is leptin deficiency. Leptin A hormone produced in cells and the placenta. Leptin regulates weight by signaling the brain to eat less when the body *** is over-stored. If, for some reason, the body does not produce enough leptin or leptin does not indicate that the brain is eating less, this loss of control can lead to obesity. The role of leptin replacement as a treatment for obesity has been explored.
4-Diet high in simple carbohydrates.
The role of carbohydrates in weight gain is unclear. Carbohydrates raise blood sugar levels, which stimulates the release of insulin through the pancreas and insulin *** promotes tissue growth and leads to weight gain. Some scientists believe that simple carbohydrates (sugars, fructose, sweets, soft drinks, ****, alcohol, etc.) contribute to more weight gain than complex carbohydrates (pasta, brown rice, whole grains). Are more rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream. Vegetables, raw fruits, etc.) and insulin release after a meal is more pronounced than complex carbohydrates. Some scientists believe that this high insulin release contributes to weight gain.
5- Feeding frequency.
The relationship between eating frequency (how often you eat) and weight has been somewhat controversial. There are many reports of overweight people eating less than those of normal weight. Scientists have found that people who eat small meals four or five times a day have lower cholesterol levels and lower and / or stable blood sugar levels less frequently (two or three times a day). Big meal). One possible explanation is that small meals produce stable insulin levels, while large meals lead to higher insulin levels after larger meals.
6- Drugs
Some of the medications associated with weight gain include antidepressants (antidepressants used to treat depression), anticonvulsants (drugs used to control seizures such as carbamazepine valproate . Used in lowering blood sugar such as insulin, sulfonylureas . Some hormones such as contraceptives and many corticosteroids such as prednisone. Some high blood pressure medications and antihistamines can cause weight gain. The reason for weight gain with drugs is different for each drug. If this worries you, you should discuss your medication with your doctor rather than discontinuing the medication, as this can lead to serious side effects.
7- Psychological factors.
For some, emotions affect eating habits. Many people overeat at late night dinner, in response to feelings such as boredom, sadness, stress or anger. Although most overweight people do not have more mental disorders than normal overweight people, 30% of those treated for severe weight problems find it difficult to overeat.
8- Diseases.
Hypothyroidism, insulin resistance, polycystic syndrome and Cushing's syndrome also contribute to obesity. Some diseases, such as Prader-Willy syndrome, can cause obesity.
9- Social issues.
There is a link between social problems and obesity. Lack of money to buy healthy food or lack of safe places to walk or exercise increases the risk of obesity.
SYMPTOMS:
Although gaining a few extra pounds may seem like a small thing as far as a person’s overall health is concerned, weight can quickly reach a serious medical condition.
The symptoms of obesity can have a negative impact on one’s daily life. For adults, persistent symptoms:
- Accumulation of extra body (especially around the waist)
- Shortness of breath 2
- Sweating (more than normal)
- Snoring
- Insomnia
- Skin problems (due to accumulation of moisture in the skin layers)
- Inability to do normal physical activity (can be done easily before gaining weight)
- Fatigue (mild to severe)
- Pain (usually in the back and joints)
- Psychological effects (negative self-esteem, depression, shame, social loneliness).
Common symptoms in children and adolescents
According to the World Health Organization, more than 340 million children and adolescents between the ages of 5 and 19 were considered overweight or obese in 2016. Boston Children 's Hospital CDC reports that childhood obesity rates have tripled in the last 30 years.
Common symptoms of childhood obesity may include:
- Eating Disorders
- Adipose tissue deposits observed in this area)
- Stretch marks appear on the hips and back
- Acanthosis nigricans (black velvet skin around neck and other areas)
- Shortness of breath with physical exertion
- Sleep apnea
- Constipation
- GI reflux
- Poor self-esteem4
- Early puberty in girls / Delay in puberty in boys
- Orthopedic problems (such as flat feet or dislocated hips)
Symptoms of unhealthy obesity:
Today, morbid obesity is a growing health problem in many developed countries of the world, especially in the United States.
When a person weighs 100 pounds more than their normal body weight, BMI is 40 or higher (in the category of severe obesity), they are considered ill and obese.
A person with a BMI of 35 or higher who has experienced obesity-related health conditions (such as high blood pressure or diabetes) is also considered ill and obese.
Unhealthy obesity causes a person to struggle with tasks such as daily activities such as walking and shortness of breath. It puts a person at high risk for many other serious health conditions.
Few Rare Symptoms:
Children develop premature obesity due to a number of rare genetic disorders involving genes that play a key role in controlling hunger and energy expenditure, including:
- Pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) Deficiency Obesity: (high appetite) among the main symptoms begins in childhood, initially with obesity and hormonal problems (such as adrenal insufficiency).
- Leptin Receptor (LEPR) Deficiency Obesity: Hyperphagia, severe early-onset obesity, and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (a condition in which the male or female ovaries produce less or no hormone due to a problem in the pituitary or gland) hypothalamus.
- Bardet-Beadle Syndrome (BBS): The main symptoms are premature obesity, hyperphagia, loss of vision, polydactyly (extra finger or toe) and kidney weakness.
Childhood obesity is a complex health problem.
This occurs when the child is over normal or healthy weight for their age and height. The causes of overweight in youth are similar in adults, including behavior and genetics. Obesity also affects an individual’s society because it affects their ability to make healthy choices.
Behaviors that affect high weight gain include high calorie, low nutrient foods and beverages, drug use and sleep routines. Lack of adequate physical activity and sedentary activities such as spending too much time on television or other screen equipment can lead to weight gain.
In contrast, eating a healthy diet and being physically active can help children grow and maintain a healthy weight. Balancing the energy or calories consumed from foods and beverages can play a role in preventing excess weight gain. In addition, eating healthy foods and staying physically active can help prevent chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, certain cancers and heart disease.
Complications Of Obesity:
In addition to the basic symptoms of obesity, obesity also contributes to many serious health disorders, many of which are not easily detected in the early stages of the disease.
Acute health problems associated with obesity:
With high blood pressure (hypertension) or heart disease the heart finds it more difficult to pump blood to a larger surface area of the body
High Cholesterol Level (fat deposits that block arteries) ******, can lead to heart attack and other problems
(from high cholesterol level and high blood pressure)
Type 2 Diabetes (50% of cases of type 2 diabetes are directly related to obesity)
Certain types of cancer (40% of cancers are associated with obesity, according to the Centers for Disease Control)
- Asthma
- Kidney disease can be caused by chronic high blood pressure that damages the kidneys.
- Osteoarthritis due to being overweight puts extra stress on the joints, bones and muscles
- Gallbladder disease (2013 study found that every single point increase on the BMI scale increased the risk of gallbladder disease by 7%)
- Sleep apnea, because the accumulation of *** in the neck and tongue obstructs the airway
- Heartburn due to gastroesophageal reflux, myocardial hernia and excessive pressure on the valves in the upper abdomen. This allows stomach acid to leak into the esophagus.
- Obese conditions, such as cancer or high blood pressure, are called "comorbidities".
- Obesity comorbidities often lead to severe chronic disability or even death. In addition, obese people experience shorter life expectancy.
- The most encouraging information from the World Health Organization is that obesity is preventable, but first, it must be detected early in the disease process.
DIAGNOSIS
To diagnose obesity, your doctor will usually do a physical exam and recommend some tests.
These tests and examinations usually include:
1-Take your health history.
Your doctor may review your weight history, weight loss efforts, physical activity and exercise habits, eating habits and appetite control, your other conditions, medications, stress levels and other issues regarding your health. Your doctor may also review your family health history to see if you have any pre-existing conditions.
2- Routine physical examination.
This includes measuring your height; Checking important signals such as heart rate, blood pressure and temperature; Listening to your heart and lungs; And checking your stomach.
3- Calculate your BMI.
Your doctor will check your body mass index (BMI). A BMI of 30 or higher is considered obese. A number over 30 can further increase your health risks. Your BMI should be checked at least once a year as this will help identify your overall health risks and what treatments may be appropriate.
Measure your waist circumference.
Storage around your waist, sometimes called visceral *** or stomach ***, further increases your risk of heart disease and diabetes. Men with a waist measurement (circumference) of more than 35 inches (89 cm, or cm) and a waist measurement of less than 40 inches (102 cm) have higher health risks. As with BMI measurement, your waist circumference should be checked at least once a year.
Checking for other health issues.
If you know of any health problems, your doctor will diagnose them. Your doctor will also check for other health problems such as high blood pressure and diabetes. Your doctor may also recommend some heart tests, such as an electrocardiogram.
Blood test.
Which tests you should take will depend on your health, risk factors and your current symptoms. Blood tests may include a cholesterol test, liver function test, fasting glucose test, thyroid test, and others.
TREATMENT:
1- Change in your lifestyle
Obesity is managed and treated to reduce the health risks posed by obesity and to improve quality of life. An appropriate weight management program usually combines changes in physical activity, healthy eating and daily habits. Other programs may include psychological counseling and in some cases drug treatment. Losing weight and keeping it away is very challenging because it requires changes in lifestyle and behavior.
2- It is important to eat a healthy, balanced diet
Fad and crash diets do not work and can be dangerous. The body needs minimal energy from food to function normally. A daily diet of less than 1000 to 1200 calories should not be taken without medical supervision. "Crash diets" are never successful in the long run because once the diet is stopped, the weight usually returns. Commercial weight loss plans and clinics are successful businesses because they have many clients.
Exercise 30 minutes daily
Successful weight loss, and maintaining a healthy weight, requires lifelong changes in diet and exercise habits, as well as understanding the emotional factors that lead to overeating. It also includes setting and achieving specific and realistic goals. People who are medically obese should consult a doctor or dietitian for a safe and personalized weight loss program. Behavioral therapy or correction may also help. Seeing a therapist or counselor can help you understand the psychological and psychological causes of overeating and teach you how to manage your eating triggers.
Regular physical activity is an important part of weight management.
In addition to maintaining weight, exercise can improve overall health and help reduce the risk of certain diseases such as cancer, heart disease and osteoporosis. Regular physical activity does not mean you have to go to the nearest gym. Instead of taking the elevator, walking or cycling and leaving the car at home, it is much easier to climb stairs (if possible) or go for a lunch time walk with colleagues. It is important to include exercise in your daily routine and work to a high level of activity. Choose activities and exercises that you enjoy.
Medications may be part of a weight management program
Medications are not "magic cures" that can lead to permanent weight loss. They are usually used in combination with a proper diet and exercise program. They are only for people who are classified as obese (i.e., those with a BMI over 30) or those with a BMI 27 and for additional risk factors for additional heart disease such as high cholesterol or diabetes.
Some drugs are approved for short-term use only. Orlistat * is an example of a weight loss drug available in Canada that inhibits absorption from to Liraglutide, an ira drug primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes, can also be used for weight loss because it reduces appetite and food intake. A combination of naltrexone and bupropion can be used to help with weight loss. Naltrexone is believed to help suppress appetite, while bupropion (traditionally used as an antidepressant) alters the amount of certain chemicals in the brain to reduce food intake. Talk to your doctor about whether medications are an option for you. Surgery will only be considered if other weight management options are not successful. There are many forms of obesity surgery, but most often surgery reduces the size of the stomach so that small amounts of food can be eaten comfortably. Some words used to describe surgery used to treat obesity are:
- Gastric surgery
- Gastric bypass surgery
- Laparoscopic band surgery
- Roux-N-Y Gastric Bypass
- Belly "staple"
HOMOEOPATHIC TREATMENT FOR OBSESS PEOPLE:
1. Calcarea carbonica:
This medicine is very useful for people who are overweight in the middle. This medicine is especially recommended for people who sweat profusely at night. It is also good for **** and weak obese children. It is recommended under the following features.
- Sweat on forehead and palm
- Severe anxiety levels
- Vertigo
- Frightened at night
- Difficulty in breathing
- Feels hungry after eating
2. Lycopodium:
It is good for overweight people due to hypothyroidism. It plays an important role in weight loss. It is given to people who have weight problems due to gastric and liver problems, which can lead to constipation and flatulence. The drug is suitable for those who have *** accumulation in the thighs and buttocks area. Such people have a strong desire for sweet and hot drinks.
3. Ammonium Mur:
This homeopathic medicine medicine is prescribed for people with slim bodies, large buttocks and slender legs. Homeopathy practitioners prescribe the prescribed medicine under the following symptoms.
- Sudden anger
- The tendency to grieve but is rare
- Severe heel pain
4. Ammonium Carb:
This homeopathic medicine is prescribed for the following symptoms:
- Heart problems
- Nervous personality
- Nose mound
- Depression
- Not satisfied with life
5. Natrum Mur:
Natrum Moore is an effective medicine for obesity and overweight. It is given under the following conditions:
- More Accumulation and weight gain in thigh and buttocks areas.
- Feeling restless and impatient with hot radiation
- Depression and stress can lead to obesity
- Good for anemia patients
- Fat people who like salt
- Crying in Depression
6. Antimonium Cradum:
Homeopathic doctors prescribe this medicine in these physical conditions:
- Obese or overweight children and adolescents
- More sensitive people
- The tongue has thick white layers
- Discolored nails
- Cravings for more salt, salty products and pickles
- Blistering common
- The best medicine for high irritability patients
- Children suffering from diarrhea and constipation due to stomach problems
7. Phytolacca:
This homeopathic medicine is prescribed for people who are overweight. It is given in the following physical conditions.
- Dry throat
- Difficult to swallow
- Common pain
- The whole body feels itchy
- Blistered tongue
- Withered face
- Hip pain
8. Graphites:
If you want to reduce excess from your body, taking this taking medicine is the wise course of action. This medicine should be taken under the following symptoms.
- Fatigue
- Cycle disorder
- Itching
- Gas formation
- Melancholy
- Abdominal pain
- Swelling genitals
9. Nux Vomica:
This generally medicine is usually given to those who lead a sedentary lifestyle with the wrong diet. This medicine should be taken under the following symptoms.
- Regular constipation
- Cold tolerant
- Craving for spicy and fried food
- People who get angry quickly
10. Focus:
Fucus is a beneficial drug for obese and overweight people. It helps in improving digestion and relieving constipation.
ALWAYS USE HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICINES AFTER SYMPTOMS AND DOCTOR'S ADVISE.NEVER USE ANY MEDICATION YOURSELF.
FOR MORE DETAIL VISIT LINK:
'
















0 Comments