- STOMACH ULCER DEF:
- TYPES OF STOMACH ULCER
- MAIN REASONS & CAUSES.
- SYMPTOMS
- DIAGNOSIS
- TREATMENT
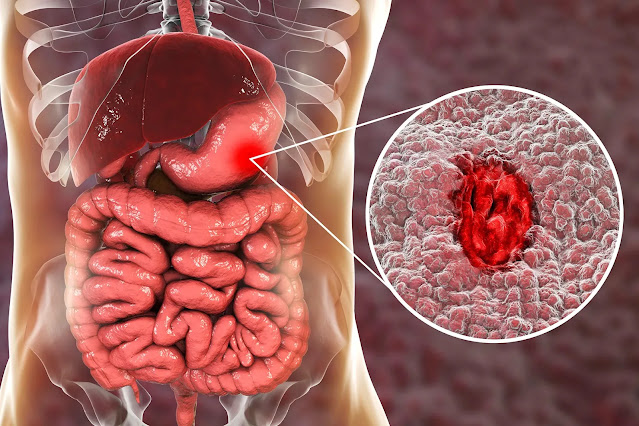
Stomach ulcers, also known as stomach ulcers, are painful stomach ulcers. Gastric or peptic ulcer: It is a type of ulcer. Peptic ulcers any ulcers that affect the stomach and small intestine.
Stomach ulcers occur when the thick layer of mucus that protects your stomach from digestive juices is reduced. This allows the digestive acids to absorb the full tissue in the stomach, causing ulcers.
Stomach ulcers can be easily treated, but they can be strong without proper treatment.
Ulcer can also appear in the intestinal tract just beyond the abdomen. These are known as duodenal Ulcer .Both abdomen and duodenal ulcers are sometimes called peptic Ulcers.
Painful sores on the protective lining of the digestive tract in humans.
The digestive tract is made orally. Stomach duodenum and intestinal ulcers are easy to treat, but can cause problems if left untreated.
TYPES OF ULCER:
Different Types Of Sores/Ulcer
While the most common types of ulcers are ulcers, there are many types, including:
- body ulcers
- vascular ulcers
- oral ulcers
- genital sores
- Peptic ulcers
Peptic ulcers are sores or ulcers that grow deep inside your stomach, the upper part of your small intestine, or your gut. Build up when digestive juice damages the walls of your stomach or intestines.
Peptic ulcers are often caused by inflammation after infection with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria and long-term use of painkillers.
There are three types of ulcers with peptic ulcers:
stomach ulcers, or ulcers that grow on the lining of the stomach
constipation sores, or sores growing on the throat
duodenal ulcers, or ulcers growing in the duodenum (small intestine)
The most common symptom of this condition is excruciating pain. Other symptoms may include:
- constipation or a feeling of satiety
- to bind
- heartburn
- nausea
- to clean
- unexplained weight loss
- chest pain
Treatment depends on the cause of your wound. If you have H. pylori infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to kill harmful germs.
If your sores have developed as a result of long-term use of painkillers or medication, your doctor may prescribe medication to reduce your stomach upset or to cover your stomach to prevent acid damage.
Vascular ulcers:
Arterial (ischemic) ulcers are open sores that grow mainly on the outer side of the ankle, feet, toes and heels. Arterial lesions develop from vascular damage due to a lack of blood flow to the muscles. These types of sores can take months to heal and require proper treatment to prevent infection and other complications.
Vascular ulcers have a "swollen" appearance that accompanies many symptoms, including:
- red, yellow or black sores
- hairless skin
- leg pain
- no bleeding
the affected area is cooled to the touch from a small blood circulation
Treatment of vascular ulcers depends on the underlying cause. Basic treatment involves restoring blood circulation to the affected area. While antibiotics can help reduce symptoms, your doctor may recommend surgery to increase blood flow to your tissues and organs. In more serious cases, your doctor may recommend a cut.
Venous ulcers:
Venous sores - the most common type of leg ulcers - are open sores that often form on your leg, below your knee and in the inside of your ankle. They usually develop from damage to your arteries caused by insufficient blood flow back to your heart.
In some cases, vascular ulcers cause minimal pain unless they are infected. Some conditions can be very painful.
Other symptoms you may experience include:
- inflammation
- itchy skin
- scratching
- discharge
Venous ulcers can take months to heal completely. In rare cases, they may not recover. Treatment focuses on improving the flow to the affected area. Antibiotics can help prevent infection and reduce symptoms, but they are not enough to heal ulcers.
In conjunction with medication, your doctor may recommend surgery or treatment for depression
Mouth sores:
Mouth sores are small sores or sores that grow on your mouth or under your gums. They are best known as corn cobs.
These sores are caused by a number of causes, including:
- biting inside your cheek
- food allergies
- brushing hard teeth
- hormonal changes
- vitamin deficiencies
- bacterial infections
- diseases
Oral ulcers are common and usually disappear within two weeks. They may be uncomfortable but should not cause too much pain. If the mouth ulcer is severe or does not go away within two weeks, seek medical help immediately.
Small mouth sores appear as small, round sores that do not leave scars. In severe cases, they can grow into large and deep wounds. Other negative symptoms associated with this type of wound may include:
unconventional healing (lasting longer than three weeks)
sores that spread on your lips
digestion of food or drink
fever
diarrhea
Oral ulcers usually go away on their own without treatment. If they do hurt, your doctor or dentist may prescribe antimicrobial cleansers or ointments to reduce your discomfort.
If your condition is the result of a serious illness, seek medical attention for the best possible treatment.
Genital Sores:
Genital sores are sores that grow on the genitals, including the penis, vagina, anus or the surrounding area. They are usually caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs), but genital sores can also be caused by trauma, inflammatory diseases, or allergies to skin care products.
In addition to sores, symptoms that may be associated with genital sores include:
- rashes or lumps in the affected area
- pain or itching
- swollen glands in the area of pain
- fever
As with most types of ulcers, treatment depends on the cause of your condition. In some cases, these lesions will go away on their own. If you are diagnosed with an STI, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics or antimicrobials or ointments. If you feel you have been exposed to an STI, seek medical help immediately.
youtube : Dr. Tayyiba AJ












1 Comments
👍👍👍
ReplyDelete