WHAT IS CATATACT? MAIN CAUSE ? TYPES OF CATARACT, SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS, HOW CAN YOU TREAT? CATARACT VISION, TREATMENT
- CATARACT DEF: / MEANING
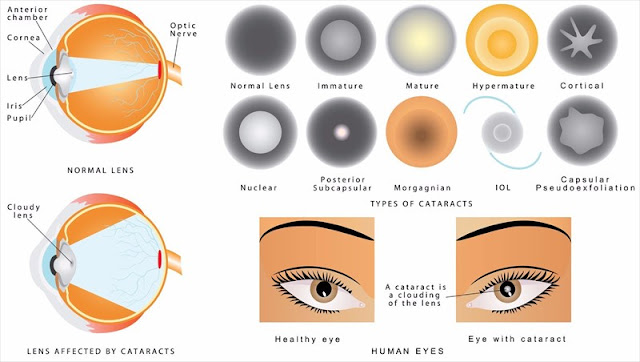
- TYPES OF CATARACT
- MAIN CAUSES
- SIGN AND SYMPTOMS
- HOW CAN BE TREATED?
- CATARCT VISION
- DIAGNOSIS
- TREATMENT
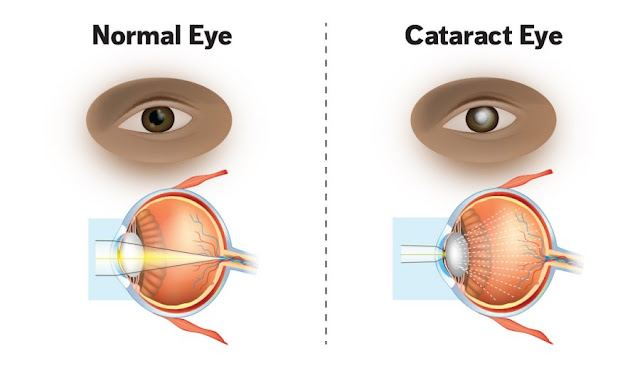
CATARACT DEF:
Your eye lens is mostly water and protein. Over time the proteins break down and they rotate in your eyes. These dull proteins can cloud your lens, so it's hard to see clearly. This is a common - albeit unpleasant - part of aging.
Some things that accelerate the formation of cataracts are:
- Diabetes.
- Common medications to treat conditions such as steroids, arthritis and lupus.
- Phenothiazine drugs such as chlorpromazine (thorazine as) are used to treat various conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
- Eye surgery or eye injury.
- Radiation therapy for your upper body.
- Spending more time in the sun without eye protection like sunglasses.
- Vision that is blurred, blurred, or blurred
- Growing difficulty with night vision
- Sensitivity to light and light
- Bright light is needed for reading and other activities
- Looking at the “hollows” around the lights
- Frequent change of prescription for glasses or contact lenses
- Paleness / fading
- Double vision in one eye
HOW CAN U TREAT CATARACT?
Surgery is the only way to treat cataracts, but you may not need it right away. If you find the problem at an early stage, you can get it with a new prescription for your glasses. A strong lens will improve your vision for a while.
What Are The Early Symptoms Of Cataract?
In the early stages, cataract can cause:
- Blurred vision:
You may notice that your vision is blurred or blurred. If your cataract is small, blurred vision may not come. Some even get double vision.
- Blurred colors:
Your cataract colors may not be as bright.
- Sensitivity:
Increases glare and bright light when cataracts occur. You can also watch the halo at night.
- Dim:
Suddenly all your lights seem to have reduced wattage? Cataracts make it difficult to read or do other tasks in low light.
- Night vision problems:
Cataracts can also affect your night vision and make it harder to see when you drive around Brandon or Plant City at night, especially if you see hollows around the lights.
- Need new glasses and contact lenses:
If you have cataracts you may notice that you need to change your glasses and contact lens prescriptions more often than in previous years.
CATARACT VISION:
Cataract is a cloud of light that is usually clear to the eye. For people with cataracts, looking through a cloudy lens is like looking through a frosty or foggy window. Glaucoma can make blurred vision difficult to read, drive a car (especially at night) or see expressions on a friend's face.
Most cataracts develop slowly and do not damage your vision quickly. But over time, cataracts can eventually disrupt your vision.
First, strong light and glasses can help you deal with cataracts. But if poor vision interferes with your normal activities, you may need cataract surgery. Fortunately, cataract surgery is usually a safe, effective procedure.
DIAGNOSIS:
To find out if you have cataract, your doctor will review your medical history and symptoms and perform an eye exam. Your doctor may perform several tests, including:
- Visual acuity test.
The visual acuity test uses an eye chart to measure how well you can read a series of letters. Your eyes will be examined one by one, the other eye will be covered. Using a small-scale chart or viewing device, your eye doctor will determine if you have 20/20 vision or if there are signs of damage in your vision.
- Wedge-lamp test.
The slit lamp allows you to see the structures in front of your eye under the magnification of your ophthalmologist. The microscope is called a slit lamp because it uses intense light and cleavage to illuminate your cornea, iris, lens and the space between your iris and cornea. The cleft allows your doctor to see these structures in small sections, making it easy to spot any minor abnormalities.
- Retinal examination.
To prepare for a retinal exam, your ophthalmologist will place drops in your eyes to dilate (expand) your pupils. This makes it easier to examine the back of your eye (retina). Using a special device called a slit lamp or ophthalmoscope, the ophthalmologist can examine your lens for cataract signals.
- Application tonometry.
This test measures the fluid pressure in your eye. There are many different tools available to do this.
- Pupil Dilation.
Pupil dilatation is a common test used in the diagnosis of glaucoma. However, as your eye widens, the pupil size increases, allowing for your overall lens view. By thoroughly examining the lens, the doctor can determine if the cataract is affecting the quality of your vision.
Although cataracts are associated with aging in many people, cataracts can also develop after an eye injury, as a result of another eye disease, after taking certain medications, including steroids, or as a result of health problems such as diabetes. . Because some babies are born with congenital cataracts, you may need to test your baby for cataracts if you think your baby has an eye problem. Subsequent tests can help determine what type of cataract is present and whether cataract surgery or another treatment may be prescribed.
- Contrast sensitivity.
Contrast Sensitivity Testing is similar to Visual Acidity Testing, but focuses more on glaucoma light scattering and how glaucoma reduces image contrast due to glare.
TREATMENT:
When to consider cataract surgery
Talk to your ophthalmologist about whether surgery is right for you. Many ophthalmologists suggest considering cataract surgery when your cataract begins to affect your quality of life or interferes with your ability to perform normal daily activities such as reading or driving at night.
It is up to you and your doctor to decide when cataract surgery is right for you. Most people have no rush to remove cataracts because they usually do not harm the eyes. But glaucoma can be more severe in people with certain conditions, including diabetes, high blood pressure or obesity.
If you decide to have cataract surgery later, delaying the procedure will not affect how well your vision improves. Take the time to discuss the benefits and risks of cataract surgery with your doctor.
If you currently choose not to have cataract surgery, your ophthalmologist may recommend periodic follow-up tests to see if your cataract is progressing. How often you see your eye doctor depends on your condition.
- What happens during cataract surgery
Two stages of cataract surgery
Open the cataract surgery pop-up dialog box
- Cataract surgery involves removing the cloud lens and replacing it with a clear artificial lens. An artificial lens called an intraocular lens is placed where your natural lens is. It is a permanent part of your eye.
For some, other eye problems limit the use of artificial lenses. In these situations, after the cataract is removed, vision can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
- Cataract surgery is usually done on a patient basis, which means you do not have to stay in the hospital after surgery. During cataract surgery, your ophthalmologist will use a local anesthetic to numb the area around your eye, but you will usually stay awake during the procedure.
- Cataract surgery is usually safe, but there is a risk of infection and bleeding. Cataract surgery increases the risk of retinal detachment.
- After the procedure, you may experience some discomfort for a few days. Healing usually occurs within a few weeks.
- If you need cataract surgery on both eyes, your doctor will schedule surgery to remove the cataract in your eye after you have recovered from the first surgery.
First Aid
1.Calcarea Carbonica
This remedy may be prescribed when a person with cataracts has a sensation seen through the fog. The person who needs this compensation is a responsible person, but is frustrated when stressed and fearful of a breakup or illness. Other signs of carbonica include chills, swollen glands, weight problems and light fatigue from work.
2.Calcrea Florica
This remedy is often prescribed when the tissue becomes stiff or abnormally thick. The person in need of this remedy may also have a tendency to have swollen lymph nodes, joint pains, fibrous growths or - spurs. Usually during a towel change the person is usually worse and improves with heat.
3. Causticum
This remedy is useful in some cases when a person with cataracts has problems with eye movement, the muscles around the eyeball are tight or weak - especially after exposure to cold air or open air. The person may have a feeling of sand in the eyes. A person in need of this remedy may have muscle stiffness in many parts of his body. They are generally better than cold and hot and often feel better in humid or rainy weather.
4. Silica (also known as silica)
This remedy is useful for some people who have glaucoma after suppressing the eyelid or foot sweat. People who need this remedy have a cold (they often have night sweats) and often have a low immunity to infection. Thin hair, weak nails, mild fatigue and swollen lymph nodes are other symptoms that indicate silicia.
Other activities:
Natrum muriaticum
This remedy may be indicated if cataract develops. The muscles around the eyes feel sore and weak, especially when the person is looking down. The person may have a foggy feeling in the eye and find it difficult to focus on certain parts of the field of vision. The person in need of this remedy usually has a craving for salt, feels more intense than being in the sun and has deep feelings, yet seems restrained.
- Phosphorus
People who need this remedy may feel blurred vision with dust or fog in the eyes or may experience stress such as eye pain after very little use. They sometimes see colorful little bright dots when they close their eyes. People who need this compensation are usually sympathetic and like company, but they can easily get tired. Active imagination (including many fears) and a strong desire for cold drinks and refreshing things are other signs for phosphorus.
FOR DETAIL VISIT MY CHANNEL
DR.TAYYIBA AJ
















1 Comments
Great 👍👍👍
ReplyDelete