WHAT IS GALLBLADDER? CAUSES, PAIN, FUNCTION, WHAT CAUSES GALLSTONE? SYMPTOMS, CAN YOU LIVE WITHOUT IT? WHAT HAPPENED AFTER GALLBLADDER REMOVE? DIAGNOSIS. TREATMENT
- GALLBLADDER DEF:
- GALLBLADDER PERFORMANCE
- PAIN OF GALLBLADDER
- GALLBLADDER INFLAMMATION
- SYMPTOMS OF GALLBLADDER
- WHAT IS MAIN CAUSES OF GALLSTONES?
- GALLSTONE SYMPTOMS
- IS IT BAD TO HAVE A BAD GALLBLADDER?
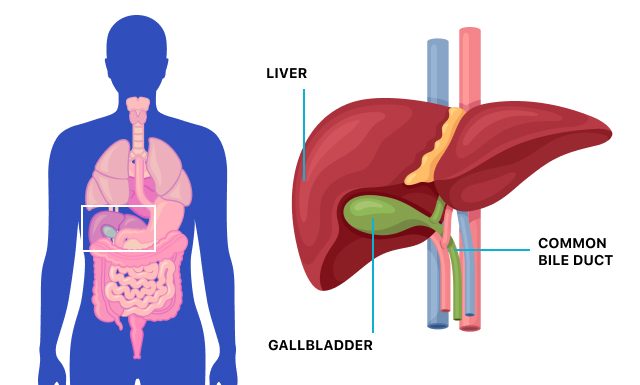
GALLBLADDER DEF:
1- Your gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped on the right side of your abdomen, just below your liver. The gallbladder contains a digestive fluid called bile that is released into your small intestine.
2- The gallbladder is a small sac located under the liver. The gallbladder stores the bile produced by the liver. After a meal, the gallbladder is empty and flattened like an inflated balloon. Before a meal, the gallbladder may be filled with bile and may be the size of a small pear.
In response to signals, the gallbladder squeezes the bile stored in the small intestine through a series of vessels called vessels. Bile helps digestion, but the gallbladder is also not needed. Gallbladder removal usually does not cause any health problems or digestive problems in a healthy person, but there is a small risk of diarrhea and fat malabsorption.
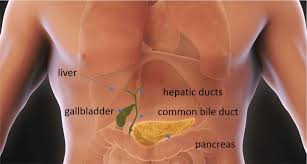
GALLBLADDER PURPOSE:
Your gallbladder is a part of your bile system, which is made up of your liver, gallbladder and appendages. This system is essential for bile production, storage and secretion.
Bile is a thick fluid that can be green, brown or yellow. It is used to aid the digestion of fats and is produced by your liver. It is estimated that your liver can produce 27 to 34 ounces of bile per day.
During a meal, bile travels directly from the liver to the small intestine. However, when you do not eat, it should be stored somewhere until it is needed. This is where the gallbladder comes in.
The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile. When you eat fatty foods, the gallbladder contracts and releases bile stored in the small intestine.
WHAT CAUSES OF GALLBLADDER PAIN?
Every time you eat, your gallbladder releases a green fluid called bile to help your body digest fats and vitamins. It flows into your small intestine through vessels called bile ducts. When something goes wrong in your gallbladder or bile ducts, the right upper part of your abdomen can be injured. You may also feel:
- Pain in your back or chest, especially when you take deep breaths
- Fever
- Like throwing
- Bloated
- Itching
- Tired
Other common symptoms include yellowing of the skin and eyes (called jaundice), weight loss, and discoloration.
The Reason Of Pain / Gallstones
These are the main causes of gallbladder pain. You get them when the gallbladder meets a tight mass. Gallstones can be small spots or the size of a golf ball. If they are large enough, these stones can block bile flow. This can lead to an attack of gallstones, a sudden pain in the right upper part of your abdomen.
These attacks often occur after a large steak dinner or other fatty meal and last for several hours. But most people with gallstones do not know it. These "quiet" stones do not cause problems with your limbs.
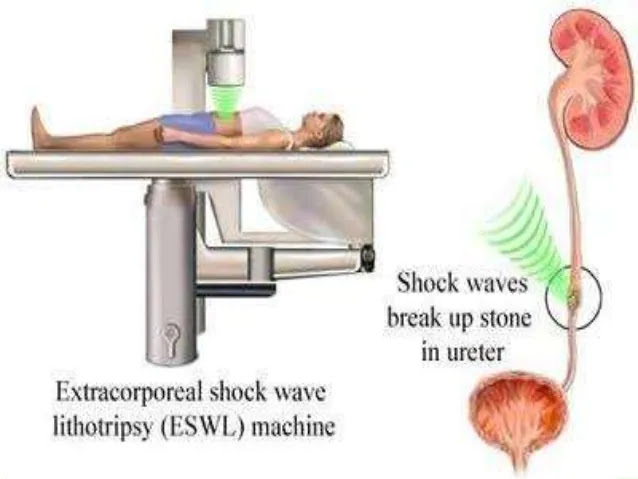
Diagnostic tests such as ultrasound, magnetic resonance (MRCP), endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), blood tests or other imaging tests can show if you have gallstones. Your doctor can also get rid of them through surgery, medicine or shock waves.
INFLAMMATION OF GALLBLADDER / CHOLECYSTITIS:
Cholecystitis, or inflammation of your gallbladder, occurs when gallstones prevent gallstones from going out of the organ. This is a very painful situation. Often, due to recurrent struggles and serious complications, surgery is the best treatment option for the relief of chronic symptoms. Fortunately, your gallbladder is not needed and you can live a normal life without it!
Signs and symptoms of cholecystitis may include:
Most people with gallstones have no symptoms at all. In fact, it is usually not known if they have gallstones until symptoms appear. These "silent gallstones" usually do not require treatment.
Symptoms usually occur when problems develop.
- The most common symptom is pain in the right upper part of the abdomen. Because pain comes in episodes, it is often referred to as an “attack”.'
- Attacks can occur every few days, weeks or months; They can also be separated by years.
- The pain usually begins 30 minutes after a fatty or greasy meal.
- The pain is usually intense, dull and constant and lasts from one to five hours.
- It can radiate to the right shoulder or back.
- It often occurs during the night and can wake a person up from sleep.
- The person may want to turn around for pain relief, but most patients prefer to lie down and wait until the attack subsides.
Other common symptoms of gallstones include:
- Nausea and vomiting,
- Fever,
- Indigestion, Belching, Flatulence,
- Intolerance to fatty or greasy foods, and
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or whitening of the eyes)
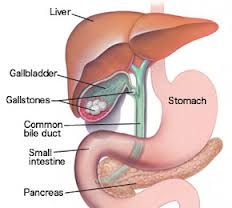
WHAT ARE GALLSTON?
Digestive fluids that form in your gallbladder are solid deposits of fluid, and range from small grains of sand (called mud) to golf balls. They are composed of cholesterol or pigment stones. Gallstones made with cholesterol are yellow-green in color and are high. Pigment stones are mostly made up of bilirubin, a substance that is formed when the liver breaks down red blood cells.
Gallstones are not the only problem. There is a possibility that you may have gallstones in your gallbladder that will never bother you and in that case you will not need treatment. However, gallstones in the gallbladder can get stuck in your vessels (tubes). They block the flow of bile from your gallbladder, causing bile to form. These events can cause the walls of your gallbladder to swell and become inflamed and this can lead to a bacterial infection in the gallbladder. Your life could be in danger unless you seek immediate medical and surgical help.
- Sudden and sharp pain in the right upper part of your abdomen
- Sudden and sharp pain in the middle of your abdomen, just below your breast bone
- Back pain between your shoulder blades
- Pain in your right shoulder
- Vomiting or nausea
- Gallbladder pain lasts from several minutes to a few hours.
- There is a lot of cholesterol in your bile
- You have a lot of bilirubin in your bile
- Your gallbladder is not emptying properly.
- Cholesterol Gall Stones
- Pigment Gallstones
- Abdominal ultrasound.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS).
- Additional Tests May Include:
- Blood Test:
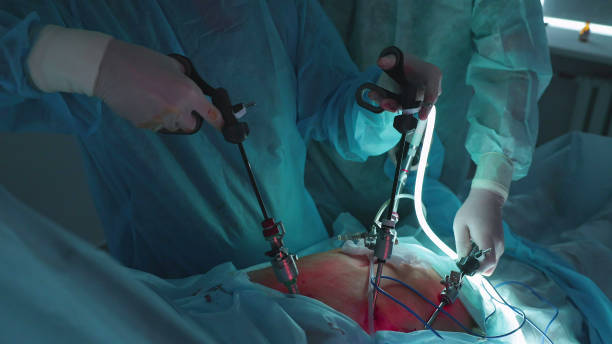
- Surgery To Remove The Gallbladder (Cholecystectomy)
- Medications To Dissolve Gallstones
- Surgery is preferred over these other treatments because if the gallbladder is not removed there is a chance of recurrence of the stone.
5. Phosphorus: For sour belching, gallstones with vomiting
Phosphorus is a natural remedy for gallstones in patients who complain of sour belching and vomiting after eating. The patient prefers soft drinks, ice cream, chicken and fish in the diet. This medicine is used to treat jaundice when the stool is very aggressive with very weakness.
Other important Homoeopathy Medicines:
The best remedies for gallstones with severe pain
- China
is an ideal natural remedy for severe gallbladder pain when the entire stomach is bloated with excess gas. Vomiting can also occur in undigested food.
- Chelidonium
is a very beneficial natural remedy when it comes to pain under the right shoulder in the shoulder.
- Berberis vulgaris
is very helpful in treating sharp, stabbing pain in the gallbladder. Pain can be exacerbated by stress. On the other hand,
- colocynth
is an ideal remedy when the pain is relieved by applying cuts, shooting nature and stress.
USE HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICINES BY DOCTOR'S ADVISE,ALWAYS USE EVERY MEDICINES AFTER DOCTOR CONSULTATION.FOR DETAIL VISIT CHANNEL










2 Comments
Nys sharing Dr
ReplyDeleteZBrdst zbrdst knwldge
ReplyDelete