WHAT IS BREAST CANCER? WHAT ARE FIVE WARNING SIGNS OF BREAST CANCER? CAN BREAST CANCER KILL YOU? IS BREAST CANCER DANGEROUS FOR LIFE? WHAT PART OF THE BREAST CANCER USUALLY FOUND? CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, DIAGMOSIS, TREATMENT
- WHAT IS BREAST CANCER?
- TYPES OF BREAST CANCER
- CAUES OF BREAST CANCER
- MAIN SYMPTOMS
- WHY IS LEFT BREAST CANCER MORE COMMON
- DIAGNOSIS
- TREATMENT
- HOW TO PREVENT BREAST CANCER
WHAT IS BREAST CANCER?
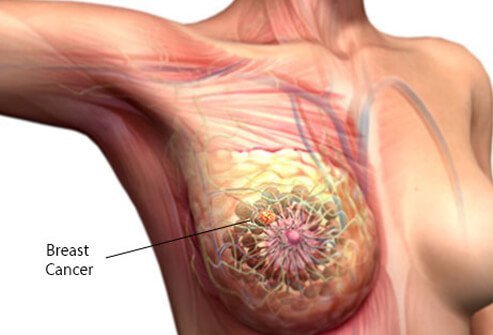
Breast Cancer is a type of cancer that starts in breast. Cancer begins when cells lose control.
Breast Cancer cells usually form a tumor, which can often be seen on X-ray or felt as a lump. Cancer occurs almost exclusively in women, but men can also get Breast cancer.
It is important to understand that most lumps are harmless and not cancerous. Non-cancerous tumors are abnormal growths, but they do not spread beyond . They are not fatal, but some types of benign cancer lumps increase the risk of cancer. Any lump or change should be checked by a health professional to find out if it is benign or malignant (cancer) and if it affects your future cancer risk.
Types Of Breast Cancer:
There are several types of cancers and they are divided into two main categories: "invasive" and "non-invasive" or situ.
While invasive cancer spreads from vessels or glands to other parts of the , non-invasive cancer does not spread from the original tissue.
These two categories are used to describe the most common types of cancer, including:
Ductal carcinoma in situ.
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive condition. With DCIS, the cancer cells are confined to the vessels in your breast and do not attack the surrounding breast tissue.
Lobular carcinoma in situ.
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is a cancer that grows in the milk-producing glands of your breast . Unlike DCIS, cancer cells do not invade surrounding tissue.
Invasive ductal carcinoma.
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) is the most common type of cancer. This type of cancer starts in your breast milk ducts and then attacks nearby tissues in breast. Once the breast cancer has spread to the tissues outside your mammary glands, it can spread to other nearby organs and tissues.
Invasive lobular carcinoma.
Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) first develops in the lobules of your breast and attacks the surrounding tissues.
Other, less common types of breast cancers:
Paget disease of nipple.
This type of breast cancer starts in the vessels, but as it grows, it affects the areola of the skin and starts from ducts of nipple.
Phyllodes tumor.
This very rare type of cancer grows in the connective tissue of breast. Most of these tumors are benign, but some are cancerous.
Angiosarcoma.
It is a cancer that grows on the blood vessels or lymphatic vessels in breast.
CAUSES OF BREAST CANCER
Doctors know that breast cancer comes when some breast cells start to grow abnormally. These cells divide faster than healthy cells and continue to accumulate, forming a lump or mass. Cells can spread through to your lymph nodes or other parts of your body (metastasize).
This type Cancer often begins in cells in the milk-producing vessels (invasive ductal carcinoma). This Cancer begins in glandular tissue called lobules (invasive lobular carcinoma) or in other cells or tissues within breast.
Researchers have identified hormones, lifestyle and environmental factors that increase your breast cancer risk. But it is not clear why some people who do not have risk factors get cancer, while others who are at risk do not. Breast Cancer is caused by the complex interaction of your genetic makeup and your environment.
1- Inherited breast cancer
Doctors estimate that 5 to 10 percent of breast cancers are associated with genetic mutations passed down through the generations in the family.
Several genetically modified genes have been identified that increase the likelihood of cancer. The most well-known are breast Cancer Gene 1 (BRCA1) and this Cancer Gene 2 (BRCA2), both of which significantly increase the risk of both breast cancer and ovarian cancer. .
If you have a strong family history of breastcancer or other cancers, your doctor may recommend blood tests to help detect specific mutations in the BRCA or other genes passed down through your family. Could not.
Ask your doctor to refer you to a genetic counselor who can review your family health history. A genetic counselor can also discuss the advantages, disadvantages, and limitations of genetic testing to help you make a partnership decision.
A Breast Cancer Risk Factors
You are more likely to get breast cancer. But having one or more cancer risk factors does not mean that you will develop breast cancer. Most women who develop cancer have no risk factors other than just women.
- Being a woman / Female
Women are more likely to get breast cancer than men.
- Aging is on the rise.
As you grow older, your risk of cancer increases.
- Personal history of circumstances.
If you have a breast biopsy that detects lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) or atypical hyperplasia, you are at risk for breat cancer
- Personal history of cancer.
If you have breast cancer one breast, you are at risk of getting cancer in another breast.
- Family history of breast cancer.
If your mother, sister or daughter suffers from breast cancer, especially at a young age, your risk of cancer increases. Still, most people with cancer have no family history of the disease.
- Hereditary genes that increase the risk of cancer.
Some genetic mutations that increase the risk of cancer are passed from parents to children. The most well-known genetic mutations are called BRCA1 and BRCA2. These genes greatly increase your risk of cancer and other cancers, but they do not make cancer inevitable.
- Radiation exposure.
If you received radiation treatment to your chest when you were a kid or teenager, your cancer risk will increase.
- Obesity.
Obesity increases your breast cancer risk.
- Your period bleeding begins at an early age
Starting your period before the age of 12 increases your breast cancer risk.
- Menopause begins in adulthood.
If you start menopause at an older age, you are more likely to get cancer.
- The birth of your first child in adulthood.
Women who give birth to their first child after 30 years are at increased risk of developing cancer.
- Never got pregnant.
Non-pregnant women have a higher risk of breast cancer than women with one or more pregnancies.
- Hormone therapy to stop menopause.
Women who take hormone therapy in combination with estrogen and progesterone to treat menopausal signs and symptoms have an increased risk of cancer. The risk of cancer is reduced when women stop taking these drugs.
- To drink alcohol
Drinking alcohol increases the risk of cancer.
TOP SEVEN WARNING SIGN /SYMPTOMS OF BREAST CANCER :
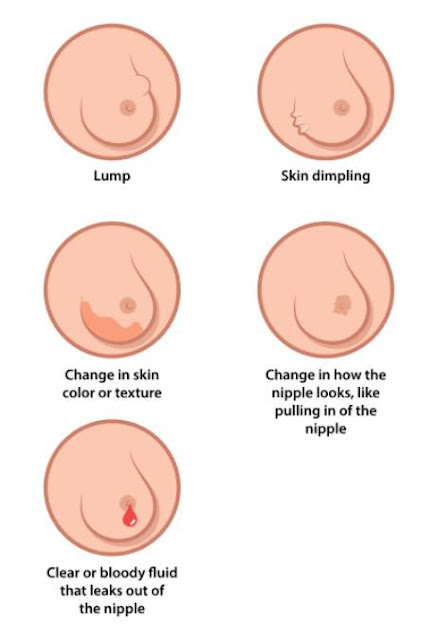
Breast Cancer manifests itself in many ways, through a variety of symptoms. For example, you may find a suspicious lump sticking to the rest of the tissue, but the lump may be soft rather than firm or rounded or painful rather than irregularly shaped. Also happens. These cases may also be breast cancer symptoms and should not be ignored as they do not fit the description of "rigid, irregularly shaped and painless".
Here are some additional features that will help you get started
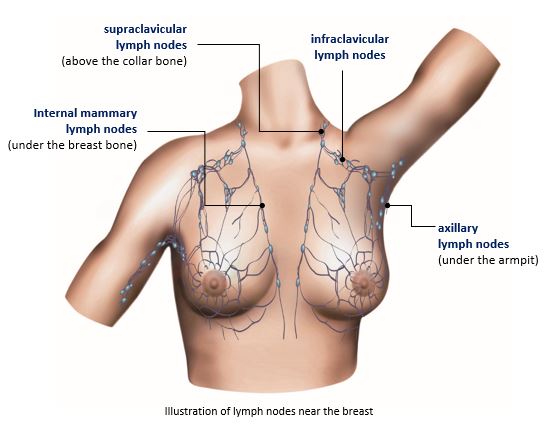
1- Swollen lymph nodes under the arm or around the collarbone
Breast Tissue covers the area under the hands and in the collarbone, and sometimes breast cancer spreads to the lymph nodes in these areas.Even if you do not feel a certain mass or lump, if you notice that any part of your breast is swollen, it may be cancer. .
3- Skin irritation or scarring.
5- Nipple retraction
You may feel your breast skin pull inward and you may notice that your skin is actually pulling as well.
7- Nipple Discharge.
Discharge may contain anything other than breast milk, and usually occurs without the squeezed, or only in the breast.
- Organ failure due to tumor size and pressure
- Complications during surgery
- Organ rupture due to tumor size
- Infections caused by the immune system's inability to fight disease during cancer treatment
In women, the cancerous lump is usually found in the breast upper quadrant.
Breast Cancer In Males:
Male breast cancer is a rare cancer of the male breast tissue. Although cancer is generally considered to be a disease that affects women, Also cancer occurs in men. Male breast Cancer can occur at any age, but is most common in the elderly.
In males, they are usually found near nipple. Regardless of gender, breast cancer can start anywhere breast tissue, from the sternum to the chin to the collarbone.
DIAGNOSIS:
Tests and procedures used to diagnose cancer:
- Breast Test.
Your doctor will examine both your breasts and the lymph nodes in your armpits, and experience any lumps or other abnormalities.
- Mammogram.
Mammograms are commonly used to diagnose cancer. If a screening mammogram reveals an abnormality, your doctor may recommend a diagnostic mammogram to further assess the abnormality.
- Breast Ultrasound.
Ultrasound uses sound waves to produce images of deep structures in the body. Ultrasound can be used to confirm that the new ****** lump is a solid mass or fluid-filled cyst.
- Removal of cell sample (biopsy) for testing breast cancer
The only way to diagnose cancer is a biopsy. During a biopsy, your doctor will use a special needle guided by an X-ray or another imaging test to remove a major portion of the tissue from the suspected area. Often, a small metal marker will remain on the site inside your, so that this area can be easily identified in future imaging tests.
Biopsy specimens are sent to a laboratory for analysis, where experts determine if the cells are cancerous. Use a biopsy sample to find out the type of cells involved in the cancer, the aggression (grade) of the cancer and whether the cancer cells have hormone receptors or other receptors that affect your treatment options. Analyzed.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
An MRI machine uses a magnet and radio waves to create images of your breast interior. Before the MRI, you will get a dye injection. Unlike other types of imaging tests, MRI does not use radiation to produce images
The tests and procedures used for the cancer stage may include:
- Blood tests such as a complete blood count
- Other mammograms look for signs of cancer
- Breast MRI
- Bone Scan
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
Not all women need all of these tests and procedures. Your doctor will select the appropriate tests based on your specific conditions and the new symptoms you are experiencing.
TREATMENT:
Some treatments remove or destroy nearby tissues such as the inside and lymph nodes. Contains:
- Surgery.
For most people, the first step is to remove the tumor. An operation called lumpectomy removes only part of your breast as cancer. This is sometimes called breast preserving surgery. In a mastectomy, doctors remove the entire breast. There are different types of mastectomy and lumpectomy.
- Radiation therapy.
This treatment uses high energy waves to beat cancer cells. Women under the age of 70 who have a lumpectomy also get radiation. The doctor may also recommend this method if the disease is contagious. It helps to destroy cancer cells that the surgeon cannot remove. Radiation may come from a machine outside your body, or there may be small seeds that emit radiation where there is a tumor inside your breast.
- Chemotherapy
Uses drugs for cancer cells. You take the medication in pills or by IV. Most people take any cancer cells left over after surgery. Doctors prescribe it before surgery to make the tumor smaller. Chemo works well against cancer, but it also damages healthy cells.
Side effects of treatment
Most breast cancer treatments have side effects. Most people leave when treatment is stopped. Some may appear later. Common side effects:
- Nausea
- Weight gain or loss
- Fatigue
- Swelling of the arm
- Hair fall
- Skin or nail changes
- Mouth sores
- Menopausal symptoms, such as hot flashes
- Difficulty getting pregnant
- Depression
- Insomnia
- Difficulty in thinking clearly ("chemo brain")
1- Conium mac
Konium mac. is an excellent medicine for cancer, where the mammary glands become stiff and sore. Typical breast cancer is cirrhotic adenocarcinoma, which begins in the tubes and attacks the parenchyma. Sometimes the condition is associated with inflammation of the tissues.
This area is firm and lumpy, sensitive to touch. The stinging pain is exacerbated during the night. Inflammation and stinging pain. The skin on the tumor is sticky.
Sometimes the pus comes from nipple. The ulcer is hard, almost cartilaginous. The margins are clearly serrated and irregular, associated with productive fibrosis. It also hurts to touch clothes or moving utensils. Injury to post-traumatic cancer.
2- Phytolacca decandra 200
phytolacca dec is an excellent remedy for breast cancer where the breast is hard, painful and of purple hue. Hard nodes in the breast with enlarged axillary glands. Nipples cracked, very sensitive and inverted. Bloody watery discharge from breasts.
3- Arsenic album
Effective in open ulcers that are aggressive with aggressive discharge. Ulcer with inflammation, biting pain and bloody aggressive discharge. There is great unrest and unrest. The person feels that taking Medicine drug is useless and fears death and disease.
4- Psorinum
This is effective against breast cancer with open ulcers. Aggressive discharge from ulcers. Swelling with redness Inflammation and itching around nipple.
5- Asterius Rubens 3C-
It is also effective for breast cancer in the ulcerative stage. There is severe pain. Tumor and glandular pain in this area, dull, nerve pain. , especially left .
The left side feels pulled inwards and the pain extends from the inner arm to the tip of the little finger. Numbness of hand and fingers on left side.
6- Hydrastis canadensis 3c-
Hydrastis canadensis is another excellent remedy for cancer, in which part of it hurts like knife. Nipple retracted. The cancer has receded. The glands in the orbit expand and cause pain. Cochlear implants - Breast Cancer as well as severe epilepsy and weakness.
ALWAYS USE HOMOEOPATHY MEDICINES WITH DOCTOR'S ADVISE AND COMPLETE HISTORY.FOR MORE DETAIL VISIT MY CHANEL"









0 Comments